A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Political corruption |
|---|
 |
| Concepts |
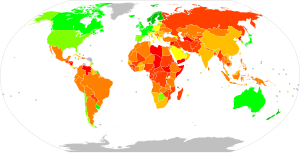
| Corruption by country |
Corruption in India is an issue which affects economy of central, state, and local government agencies. Corruption is blamed for stunting the economy of India.[1] A study conducted by Transparency International in 2005 recorded that more than 62% of Indians had at some point or another paid a bribe to a public official to get a job done.[2][3] In 2008, another report showed that about 50% of Indians had first hand experience of paying bribes or using contacts to get services performed by public offices.[4] In Transparency International's 2022 Corruption Perceptions Index, which scored 180 countries on a scale from 0 ("highly corrupt") to 100 ("very clean"), India scored 40. When ranked by score, India ranked 85th among the 180 countries in the Index, where the country ranked first is perceived to have the most honest public sector.[5] For comparison, the best score was 90 (ranked 1), the worst score was 12 (ranked 180), and the average score was 43.[6] Various factors contribute to corruption, including officials siphoning money from government social welfare schemes. Examples include the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act and the National Rural Health Mission.[7][8] Other areas of corruption include India's trucking industry, which is forced to pay billions of rupees in bribes annually to numerous regulatory and police stops on interstate highways.[9]
The media has widely published allegations of corrupt Indian citizens stashing millions of rupees in Swiss banks. Swiss authorities denied these allegations, which were later proven in 2015–2016. In July 2021, India's Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) replied to Right To Information (RTI) requests stating undeclared assets of Rs 20,078 crore identified by them in India and abroad following the investigation till June 2021.[10][11][12]
The causes of corruption in India include excessive regulations, complicated tax and licensing systems, numerous government departments with opaque bureaucracy and discretionary powers, monopoly of government controlled institutions on certain goods and services delivery, and the lack of transparent laws and processes.[13][14] There are significant variations in the level of corruption and in the government's efforts to reduce corruption across India.
Politics
Corruption in India is a problem that has serious implications for protecting the rule of law and ensuring access to justice. As of December 2009[update], 120 of India's 542 parliament members were accused of various crimes, under India's First Information Report procedure wherein anyone can allege another to have committed a crime.[15]
Many of the biggest scandals since 2010[update] have involved high level government officials, including Cabinet Ministers and Chief Ministers, such as the 2010 Commonwealth Games scam (₹70,000 crore (US$8.8 billion)), the Adarsh Housing Society scam, the Coal Mining Scam (₹1.86 lakh crore (US$23 billion)), the Mining Scandal in Karnataka, and the Cash for Vote scams.
Lack of accountability
Since the anti-corruption departments in India exist as defunct outfits, the corrupt bureaucrats and politicians keep committing acts of corruption with impunity. This fact is also stated in its annual country report released in April 2022 by the U.S. Department of State.[16]
In an exclusive section, "Corruption and Lack of Transparency in Government", the report asserts that the law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials at all levels of government in India. However, officials frequently engaged in corrupt practices with impunity while there were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.[16]
The U.S. report further reveals that a lack of accountability for official misconduct persisted at all levels of government in India, contributing to widespread impunity. While investigations and prosecutions of individual cases took place, lax enforcement, a shortage of trained police officers, and an overburdened and under-resourced court system contributed to a low number of convictions, the report said.[16]
The U.S. report adds that corruption in India happens at different levels including the payment of bribes to expedite services such as police protection, school admission, water supply, and government assistance.[16]
Bureaucracy
Bribery
A 2005 study done by the Transparency International in India found that more than 62% of the people had firsthand experience of paying bribes or peddling influence to get services performed in a public office.[3] Taxes and bribes are common between state borders; Transparency International estimates that truckers annually pay ₹222 crore (US$28 million) in bribes.[9][17]
Both government regulators and police share in bribe money, to the tune of 43% and 45% each, respectively. The en route stoppages at checkpoints and entry-points can take up to 11 hours per day. About 60% of these (forced) stoppages on roads by concerned authorities such as government regulators, police, forest, sales and excise, octroi and weighing and measuring departments are for extorting money. The loss in productivity due to these stoppages is an important national concern; the number of truck trips could increase by 40%, if forced delays are avoided. According to a 2007 World Bank published report, the travel time for a Delhi-Mumbai trip could be reduced by about 2 days per trip if the corruption and associated regulatory stoppages to extract bribes were eliminated.[17][18][19]
A 2009 survey of the leading economies of Asia, revealed Indian bureaucracy to be not only the least efficient among Singapore, Hong Kong, Thailand, South Korea, Japan, Malaysia, Taiwan, Vietnam, China, Philippines and Indonesia, but that working with India's civil servants was a "slow and painful" process.[20]
Land and property
Officials are alleged to steal state property. In cities and villages throughout India, groups of municipal and other government officials, elected politicians, judicial officers, real estate developers, and law enforcement officials, acquire, develop and sell land in illegal ways.[21] Such officials and politicians are very well protected by the immense power and influence they possess. Apart from this, slum-dwellers who are allotted houses under several housing schemes such as Pradhan Mantri Gramin Awaas Yojana, Rajiv Awas Yojna, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojna, etc., rent out these houses to others, to earn money due to severe unemployment and lack of a steady source of income.
Tendering processes and awarding contracts
This section needs to be updated. (May 2023) |
A 2006 report claimed state-funded construction activities in Uttar Pradesh, such as road building were dominated by construction mafias, consisting of cabals of corrupt public works officials, materials suppliers, politicians and construction contractors.[22]
Problems caused by corruption in government-funded projects are not limited to the state of Uttar Pradesh. The World Bank study finds that the public distribution programs and social spending contracts have proven to be a waste due to corruption.[23]
For example, the government implemented the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) on 25 August 2005. The Central government outlay for this welfare scheme is ₹400 crore (US$50 million) in FY 2010–2011.[24] After 5 years of implementation, in 2011, the programme was widely criticised as no more effective than other poverty reduction programmes in India. Despite its best intentions, MGNREGA faces the challenges of corrupt officials reportedly pocketing money on behalf of fake rural employees, poor quality of the programme infrastructure, and unintended destructive effect[clarification needed] on poverty.[8][25]
Hospitals and health care
In government hospitals, corruption is associated with non-availability/duplication of medicines, obtaining admission, consultations with doctors, and receiving diagnostic services.[3]
National Rural Health Mission is another health care-related government programme that has been subject to large scale corruption allegations. This social spending and entitlement programme hoped to improve health care delivery across rural India. Managed since 2005 by the Ministry of Health, the Indian government mandated a spending of ₹2.77 lakh crore (US$35 billion) in 2004–2005, and increased it annually to be about 1% of India's gross domestic product. The National Rural Health Mission programme has been clouded by a large-scale corruption scandal in which high-level government appointed officials were arrested, several of whom died under mysterious circumstances including one in prison. Corruption, waste and fraud-related losses from this government programme has been alleged to be ₹1 lakh crore (US$13 billion).[26][27][28][7]
Science and technology
CSIR, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, has been flagged in ongoing efforts to root out corruption in India.[29] Established with the directive to do translational research and create real technologies, CSIR has been accused of transforming into a ritualistic, overly-bureaucratic organisation that does little more than churn out papers.[30][31]
There are many issues facing Indian scientists, with some, such as MIT systems scientist VA Shiva Ayyadurai, calling for transparency, a meritocratic system, and an overhaul of the bureaucratic agencies that oversee science and technology.[32][33][34] Sumit Bhaduri stated, "The challenges of turning Indian science into part of an innovation process are many. Many competent Indian scientists aspire to be ineffectual administrators (due to administrative power and political patronage), rather than do the kind of science that makes a difference".[35] Prime minister Manmohan Singh spoke at the 99th Indian Science Congress and commented on the state of the sciences in India, after an advisory council informed him there were problems with "the overall environment for innovation and creative work" and a "war-like" approach was needed.[36]
Income tax department
There have been several cases of collusion involving officials of the Income Tax Department of India for preferential tax treatment and relaxed prosecutions in exchange for bribes.[37][38]
Preferential award of mineral resources
In August 2011, an iron ore mining scandal became a media focus in India. In September 2011, elected member of Karnataka's legislative assembly Janardhana Reddy, was arrested on charges of corruption and illegal mining of iron ore in his home state. It was alleged that his company received preferential allotment of resources, organised and exported billions of dollars' worth of iron ore to Chinese companies in recent years without paying any royalty to the state government exchequer of Karnataka or the central government of India, and that these Chinese companies made payment to shell companies registered in Caribbean and north Atlantic tax havens controlled by Reddy.[39][40]
It was also alleged that corrupt government officials cooperated with Reddy, starting from government officials in charge of regulating mining to government officials in charge of regulating port facilities and shipping. These officials received monthly bribes in exchange for enabling the illegal export of illegally mined iron ore to China. Such scandals have led to a demand in India for consensually driven action plan to eradicate the piracy of India's mineral resources by an illegal, politically corrupt government officials-business nexus, removal of incentives for illegal mining, and the creation of incentives for legal mining and domestic use of iron ore and steel manufacturing.[39][40]
Driver licensing
A study conducted between 2004 and 2005 found that India's driver licensing procedure was a hugely distorted bureaucratic process and allows drivers to be licensed despite their low driving ability through promoting the usage of agents. Individuals with the willingness to pay make a significant payment above the official fee and most of these extra payments are made to agents, who act as an intermediary between bureaucrats and applicants.[41]
The average licensee paid Rs 1,080, approximately 2.5 times the official fee of Rs 450, in order to obtain a licence. On average, those who hired agents had a lower driving ability, with agents helping unqualified drivers obtain licences and bypass the legally required driving examination. Among the surveyed individuals, approximately 60% of the licence holders did not even take the licensing exam and 54% of those licence holders failed an independent driving test.[42]
Agents are the channels of corruption in this bureaucratic driver licensing system, facilitating access to licences among those who are unqualified to drive. Some of the failures of this licensing system are caused by corrupt bureaucrats who collaborate with agents by creating additional barriers within the system against those who did not hire agents.[41]
Trends
Professor Bibek Debroy and Laveesh Bhandari claim in their book Corruption in India: The DNA and RNA that public officials in India may be cornering as much as ₹921 billion (US$12 billion), or 5 per cent of the GDP through corruption.[18] The book claims most bribery is in government delivered services and the transport and real estate industries.
Bribery and corruption are pervasive, but some areas tend to have more issues than others. A 2013 EY (Ernst & Young) Study[43] reports the industries perceived to be the most vulnerable to corruption as: Infrastructure & Real Estate, Metals & Mining, Aerospace & Defence, and Power & Utilities. There is a range of specific factors that make a sector more susceptible to bribery and corruption risks than others. High use of middlemen, large value contracts, liaisoning activities, etc. drive the depth, volume, and frequency of corrupt practices in vulnerable sectors.
A 2011 KPMG study reports India's real estate, telecommunications, and government-run social development projects as the three top sectors plagued by corruption. The study found India's defence, information technology, and energy sectors to be the most competitive and least corruption-prone sectors.[13]
CMS India claims in its 2010 India Corruption Study report that socio-economically weaker sections of Indian society are the most adversely affected by government corruption. These include the rural and urban poor, although the study claims that nationwide perception of corruption decreased between 2005 and 2010. Over the 5-year period, a significantly greater number of people surveyed from the middle and poorest classes in all parts of India claimed government corruption had dropped over time, and that they had fewer direct experiences with bribery demands.[44]
The table below compares the perceived anti-corruption effort across some of the major states in India.[14] A rising index implies higher anti-corruption effort and falling corruption. According to this table, the states of Bihar and Gujarat have experienced significant improvements in their anti-corruption efforts, while conditions have worsened in the states of Assam and West Bengal. Consistent with the results in this table, in 2012 a BBC News report claimed the state of Bihar has transformed in recent years to become the least corrupt state in India.[45]
| State | 1990–95 | 1996–00 | 2001–05 | 2006–10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bihar | 0.41 | 0.30 | 0.43 | 0.88 |
| Gujarat | 0.48 | 0.57 | 0.64 | 0.69 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 0.53 | 0.73 | 0.55 | 0.61 |
| Punjab | 0.32 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.60 |
| Jammu & Kashmir | 0.13 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.40 |
| Haryana | 0.33 | 0.60 | 0.31 | 0.37 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.35 |
| Tamil Nadu | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.29 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.29 |
| Karnataka | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.29 |
| Rajasthan | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.27 |
| Kerala | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.27 |
| Maharashtra | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.26 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.21 |
| Odisha | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.19 |
| Assam | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.17 |
| West Bengal | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
Black money
Black money refers to money that is not fully or legitimately the property of the 'owner'. A government white paper on black money in India suggests two possible sources of black money in India;[11] the first includes activities not permitted by the law, such as crime, drug trade, terrorism, and corruption, all of which are illegal in India and secondly, wealth that may have been generated through lawful activity but accumulated by failure to declare income and pay taxes. Some of this black money ends up in illicit financial flows across international borders, such as deposits in tax haven countries.
A November 2010 report from the Washington-based Global Financial Integrity estimates that over a 60-year period, India lost US$213 billion in illicit financial flows beginning in 1948; adjusted for inflation, this is estimated to be $462 billion in 2010, or about $8 billion per year ($7 per capita per year). The report also estimated the size of India's underground economy at approximately US$640 billion at the end of 2008 or roughly 50% of the nation's GDP.[46]
Indian black money in Switzerland
India was ranked 38th by money held by its citizens in Swiss banks in 2004 but then improved its ranking by slipping to 61st position in 2015 and further improved its position by slipping to 75th position in 2016.[47][48] According to a 2010 The Hindu article, unofficial estimates indicate that Indians had over US$1,456 billion in black money stored in Swiss banks (approximately US$1.4 trillion).[49] While some news reports claimed that data provided by the Swiss Banking Association[50] Report (2006) showed India has more black money than the rest of the world combined,[51][52] a more recent report quoted the SBA's Head of International Communications as saying that no such official Swiss Banking Association statistics exist.[53]
Another report said that Indian-owned Swiss bank account assets are worth 13 times the country's national debt. These allegations have been denied by Swiss Bankers Association. James Nason of Swiss Bankers Association in an interview about alleged black money from India, holds that "The (black money) figures were rapidly picked up in the Indian media and in Indian opposition circles, and circulated as gospel truth. However, this story was a complete fabrication. The Swiss Bankers Association never published such a report. Anyone claiming to have such figures (for India) should be forced to identify their source and explain the methodology used to produce them."[12][54]
In a separate study, Dev Kar of Global Financial Integrity concludes, "Media reports circulating in India that Indian nationals held around US$1.4 trillion in illicit external assets are widely off the mark compared to the estimates found by his study." Kar claims the amounts are significantly smaller, only about 1.5% of India's GDP on average per annum basis, between 1948 and 2008. This includes corruption, bribery and kickbacks, criminal activities, trade mispricing, and efforts to shelter wealth by Indians from India's tax authorities.[46]
According to a third report, published in May 2012, the Swiss National Bank estimates that the total amount of deposits in all Swiss banks, at the end of 2010, by citizens of India were CHF 1.95 billion (₹92.95 billion (US$1.2 billion)). The Swiss Ministry of External Affairs has confirmed these figures upon request for information by the Indian Ministry of External Affairs. This amount is about 700-fold less than the alleged $1.4 trillion in some media reports.[11] The report also provided a comparison of the deposits held by Indians and by citizens of other nations in Swiss banks. Total deposits held by citizens of India constitute only 0.13 per cent of the total bank deposits of citizens of all countries. Further, the share of Indians in the total bank deposits of citizens of all countries in Swiss banks has reduced from 0.29 per cent in 2006 to 0.13 per cent in 2010.
Domestic black money
Indian companies have been reported to misuse public trusts for money laundering. India has no centralised repository—like the registrar of companies for corporates—of information on public trusts.[55]
2016 Evasion attempts after note ban

- Gold purchases
In Gujarat, Delhi and many other major cities, sales of gold increased on 9 November, with an increased 20% to 30% premium surging the price as much as ₹45,000 (US$560) from the ruling price of ₹31,900 (US$400) per 10 grams (0.35 oz).[56][57]
- Donations
Authorities of Sri Jalakanteswarar temple at Vellore discovered cash worth ₹4.4 million (US$55,000) from the Hindu temple .[58]
- Multiple bank transactions
There have also been reports of people circumventing the restrictions imposed on exchange transactions and attempting to convert black money into white by making multiple transactions at different bank branches.[59] People were also getting rid of large amounts of banned currency by sending people in groups to exchange their money at banks.[60] In response, the government announced that it would start marking customers with indelible ink. This was in addition to other measures proposed to ensure that the exchange transactions are carried out only once by each person.[61][62][63] On 17 November, the government reduced the exchange amount to ₹2,000 (US$25) to discourage attempts to convert black money into legitimate money.
- Railway bookings
As soon as the demonetisation was announced, it was observed by the Indian Railways authorities that a large number of people started booking tickets particularly in classes 1A and 2A for the longest distance possible, to get rid of unaccounted-for cash. A senior official said, "On November 13, 42.7 million passengers were nationally booked across all classes. Of these, only 1,209 were for 1A and 16,999 for 2A. It is a sharp dip from the number of passengers booked on November 9, when 27,237 passengers had booked tickets in 1A and 69,950 in 2A."[64] The Railways Ministry and the Railway Board responded swiftly and decided that cancellation and refund of tickets of value ₹10,000 and above will not be allowed by any means involving cash. The payment can only be through cheque/electronic payment. A copy of the PAN card must be submitted for any cash transaction above ₹50,000. The railway claimed that since the Railway Board on 10 November imposed a number of restrictions to book and cancel tickets, the number of people booking 1A and 2A tickets came down.[64][65]
- Municipal and local tax payments
As the use of the demonetised notes had been allowed by the government for the payment of municipal and local body taxes, leading to people using the demonetised ₹500 and ₹1,000 notes to pay large amounts of outstanding and advance taxes. As a result, revenue collections of the local civic bodies jumped. The Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation reported collecting about ₹1.6 billion (US$20 million) in cash payments of outstanding and advance taxes within 4 days.[66]
- Axis Bank
Income Tax officials raided multiple branches of Axis Bank and found bank officials involved in acts of money laundering.[67][68][69]
Business and corruption
Public servants have very wide discretionary powers offering the opportunity to extort undue payments from companies and ordinary citizens. The awarding of public contracts is notoriously corrupt, especially at the state level. Scandals involving high-level politicians have highlighted the payment of kickbacks in the healthcare, IT and military sectors. The deterioration of the overall efficiency of the government, protection of property rights, ethics and corruption as well as undue influence on government and judicial decisions has resulted in a more difficult situation for business environment.[citation needed]
Judiciary
According to Transparency International, judicial corruption in India is attributable to factors such as "delays in the disposal of cases, shortage of judges and complex procedures, all of which are exacerbated by a preponderance of new laws".[70] Over the years there have been numerous allegations against judges, and in 2011 Soumitra Sen, a former judge at the Calcutta High Court became the first judge in India to be impeached by the Rajya Sabha, (Upper House of the Indian Parliament) for misappropriation of funds.[71]
Anti-corruption initiatives
Right to Information Act
The 2005 Right to Information Act required government officials to provide information requested by citizens or face punitive action, as well as the computerisation of services and the establishment of vigilance commissions. This has considerably reduced corruption and opened up avenues to redress grievances.[3]
Right to Public Services laws
Right to Public Services legislation, which has been enacted in 19 states of India, guarantee time bound delivery of services for various public services rendered by the government to citizen and provides mechanisms for punishing the errant public servant who is deficient in providing the service stipulated under the statute.[72] Right to Service legislation is meant to reduce corruption among the government officials and to increase transparency and public accountability.[73]
Anti-corruption laws in India
Public servants in India can be imprisoned for several years and penalised for corruption under the:
- Indian Penal Code, 1860
- Prosecution section of Income Tax Act, 1961
- The Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988
- The Benami Transactions (Prohibition) Act, 1988 to prohibit benami transactions.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002
Punishment for bribery in India can range from six months to seven years of imprisonment.
India is also a signatory to the United Nations Convention against Corruption since 2005 (ratified 2011). The Convention covers a wide range of acts of corruption and also proposes certain preventive policies.[74]
The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013 which came into force from 16 January 2014, seeks to provide for the establishment of the institution of Lokpal to inquire into allegations of corruption against certain public functionaries in India.[75][76]
Whistle Blowers Protection Act, 2011, which provides a mechanism to investigate alleged corruption and misuse of power by public servants and also protect anyone who exposes alleged wrongdoing in government bodies, projects and offices, has received the assent of the President of India on 9 May 2014, and (as of 2 August) is pending for notification by the Central Government.[77][78]
At present there are no legal provisions to check graft in the private sector in India. Government has proposed amendments in existing acts and certain new bills for checking corruption in private sector. Big-ticket corruption is mainly witnessed in the operations of large commercial or corporate entities. In order to prevent bribery on supply side, it is proposed that key managerial personnel of companies' and also the company shall be held liable for offering bribes to gain undue benefits.[citation needed]
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 provides that the properties of corrupt public servants shall be confiscated. However, the Government is considering incorporating provisions for confiscation or forfeiture of the property of corrupt public servants into the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 to make it more self-contained and comprehensive.[43]
A committee headed by the Chairman of Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), has been constituted to examine ways to strengthen laws to curb generation of black money in India, its illegal transfer abroad, and its recovery. "The Committee shall examine the existing legal and administrative framework to deal with the menace of generation of black money through illegal means including inter-alia the following: 1. Declaring wealth generated illegally as national asset; 2. Enacting/amending laws to confiscate and recover such assets; and 3. Providing for exemplary punishment against its perpetrators." (Source: 2013 EY report on Bribery & Corruption)
The Companies Act, 2013, contains certain provisions to regulate frauds by corporations including increased penalties for frauds, giving more powers to the Serious Fraud Investigation Office, mandatory responsibility of auditors to reveal frauds, and increased responsibilities of independent directors.[79] The Companies Act, 2013 also provides for mandatory vigil mechanisms which allow directors and employees to report concerns and whistleblower protection mechanism for every listed company and any other companies which accepts deposits from public or has taken loans more than 50 crore rupees from banks and financial institutions. This intended to avoid accounting scandals such as the Satyam scandal which have plagued India.[80] It replaces The Companies Act, 1956 which was proven outmoded in terms of handling 21st century problems.[81]
In 2015, Parliament passed the Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition of Tax Bill, 2015 to curb and impose penalties on black money hoarded abroad. The Act has received the assent of the President of India on 26 May 2015. It came into effect from 1 July 2015.
Anti-corruption police and courts
The Directorate General of Income Tax Investigation, Central Vigilance Commission and Central Bureau of Investigation all deal with anti-corruption initiatives. Certain states such as Andhra Pradesh (Anti-Corruption Bureau, Andhra Pradesh) Kerala (Vigilance & Anti-corruption Bureau, Kerala) and Karnataka (Lokayukta) also have their own anti-corruption agencies and courts.[82][83][84]
| Sr No. | State/UT | Anti-Corruption Agency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Andhra Pradesh Anti-Corruption Bureau |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | |
| 3 | Assam | Directorate of Vigilance & Anti-Corruption, Assam |
| 4 | Bihar | |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Anti-Corruption Bureau, Chhattisgarh |
| 6 | Goa | Goa Police Anti-Corruption Branch |
| 7 | Gujarat | Gujarat Anti-Corruption Bureau |
| 8 | Haryana | Haryana State Vigilance Bureau |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | Himachal Pradesh State Vigilance & Anti-Corruption Bureau |
| 10 | Jharkhand | Anti-Corruption Bureau, Jharkhand |
| 11 | Karnataka | Lokayukta,Karnataka |
| 12 | Kerala | Vigilance & Anti-Corruption Bureau, Kerala (VACB) |
| 13 | Madhya Pradesh | Lokayukta Special Police Establishment, Madhya Pradesh |
| 14 | Maharashtra | Maharashtra Anti-Corruption Bureau |
| 15 | Manipur | Vigilance & Anti-Corruption Department, Manipur |
| 16 | Meghalaya | Meghalaya Police Anti-Corruption Branch |
| 17 | Mizoram | Anti-Corruption Bureau, Mizoram |
| 18 | Nagaland | Directorate of Vigilance & Anti-Corruption Police, Nagaland |
| 19 | Odisha | Odisha Vigilance Directorate |
| 20 | Punjab | Punjab State Vigilance Bureau |

